The United Nations (UN) relies heavily on military and law enforcement personnel from Africa and experts from African countries for its missions. These experts are assigned special missions that only they are qualified to carry out and are given privileges to support their successful completion of these missions.
Ensuring peace and cooperation within and beyond Africa is a top priority for countries, as external affairs can significantly impact the continent. As a result, African peacekeepers view their UN assignments as part of a broader strategy to secure long-term stability and development for the continent.
African UN peacekeepers are uniquely qualified to undertake regular assignments or special missions, for which they are designated experts. This underscores the trust and confidence the UN places in its expertise.
According to a document released by the United Nations, experts on missions may be engaged through a consultant contract, which outlines the terms of their employment and their responsibilities. However, it’s important to note that individuals may be considered experts on missions even without signing a consultant contract, as long as they are selected by the United Nations to carry out tasks or responsibilities of the organisation.
Moreover, these experts are afforded special rights necessary to fulfil their duties for the UN, and the responsibilities of “officials” and experts on missions are not subject to government control. While some African countries have a considerable number of experts on missions, other countries have very few or none at all.
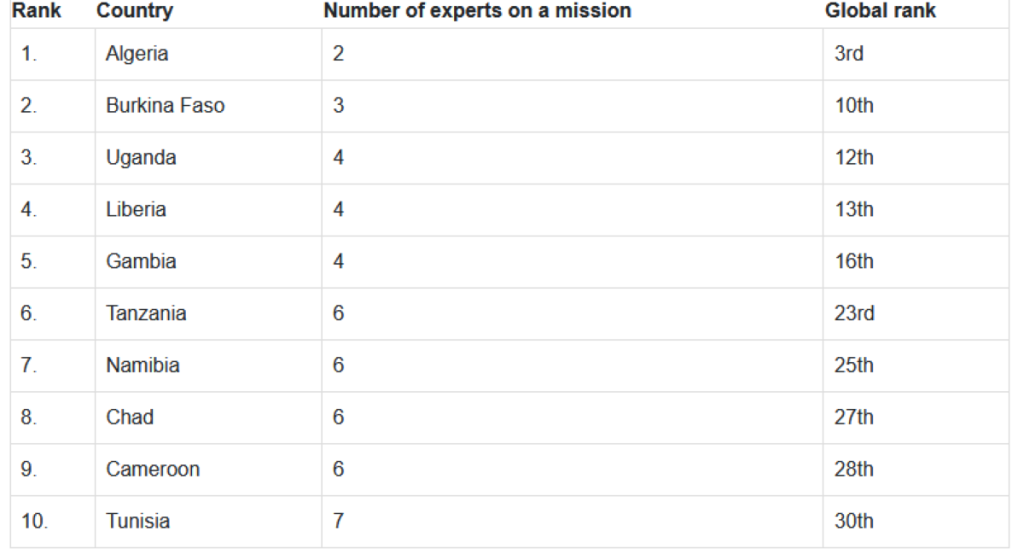
Here are the top 10 African countries with the smallest number of experts on UN missions as of mid-2024.