Central banks play a crucial role in the global economy, primarily by managing a country’s money supply and interest rates. They also regulate and supervise financial institutions within their jurisdiction. Additionally, central banks work to ensure financial stability and promote sustained economic growth.
The wealth of a central bank is typically measured by its assets, which can include gold, foreign currencies, and government bonds. Generally, the assets of central banks around the world reflect the overall health of a country’s economy.
According to the Sovereign Wealth Fund Institute (SWFI), these are the top ten richest central banks in the world;
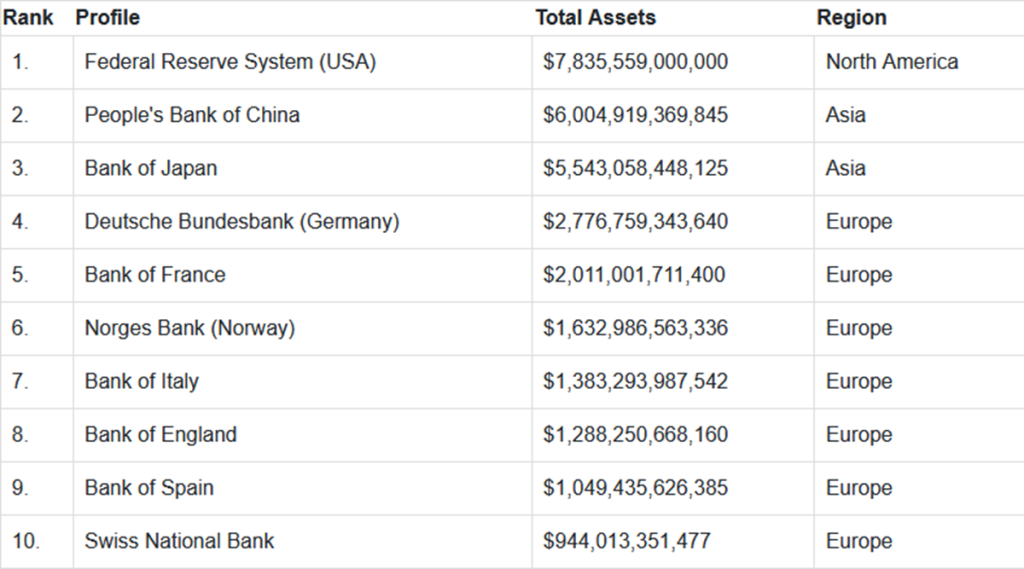
When evaluating a central bank’s assets, several factors are considered, such as the foreign exchange reserves, which encompass monetary gold, foreign exchange funds, special drawing rights (SDRs), and a reserve position in the IMF.
The exclusion of African Central banks from the aforementioned list may be attributed to the region’s challenges, including escalating inflation, vulnerable financial markets, and an ineffective monetary policy transmission system.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), African central banks can address reduced growth and increased inflation by implementing foreign exchange interventions, capital flow restrictions, and tackling underlying structural issues.


