WhatsApp currently has over two billion monthly active users, making it the most widely used messaging app globally. It is available in over 180 countries and in 60 languages, and 100 billion messages are sent on the platform every day.
Despite having a large global user base, WhatsApp is limited in some countries due to regulatory issues.
Recent reports suggest that the instant messaging app might leave Nigeria because of violations of the Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Commission (FCCPC) laws.
The FCCPC imposed a $220 million fine on WhatsApp for breaching data privacy regulations, citing allegations of user data violations.
In response to the FCCPC’s penalty, WhatsApp said it might consider “withdrawing certain services” in Nigeria.

Here are the countries where WhatsApp has been banned or restricted.
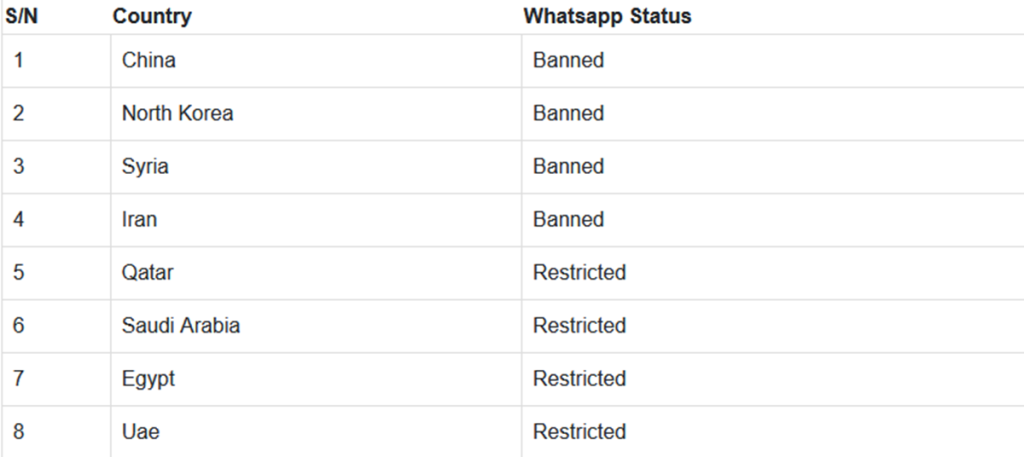
WhatsApp’s operations have been entirely blocked in China, North Korea, Syria, and Iran, leaving residents unable to send messages through the app. In other countries like Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and the UAE, while messaging remains accessible, audio and video calls have been restricted.
The outright ban in some of these nations is often justified by a desire to control information flow and support local telecommunications providers.
In Nigeria, the Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Commission (FCCPC) has investigated the app for allegedly breaching the Consumer Protection Act and the Nigeria Data Protection Regulation (NDPR). The FCCPC’s statement highlighted concerns that WhatsApp’s pre-ticked terms and conditions prevented users from opting out of data sharing and involved sharing data without explicit consent. This practice differed from the platform’s policies in other regions with similar data protection standards.


